Halting and reversing Global extinction
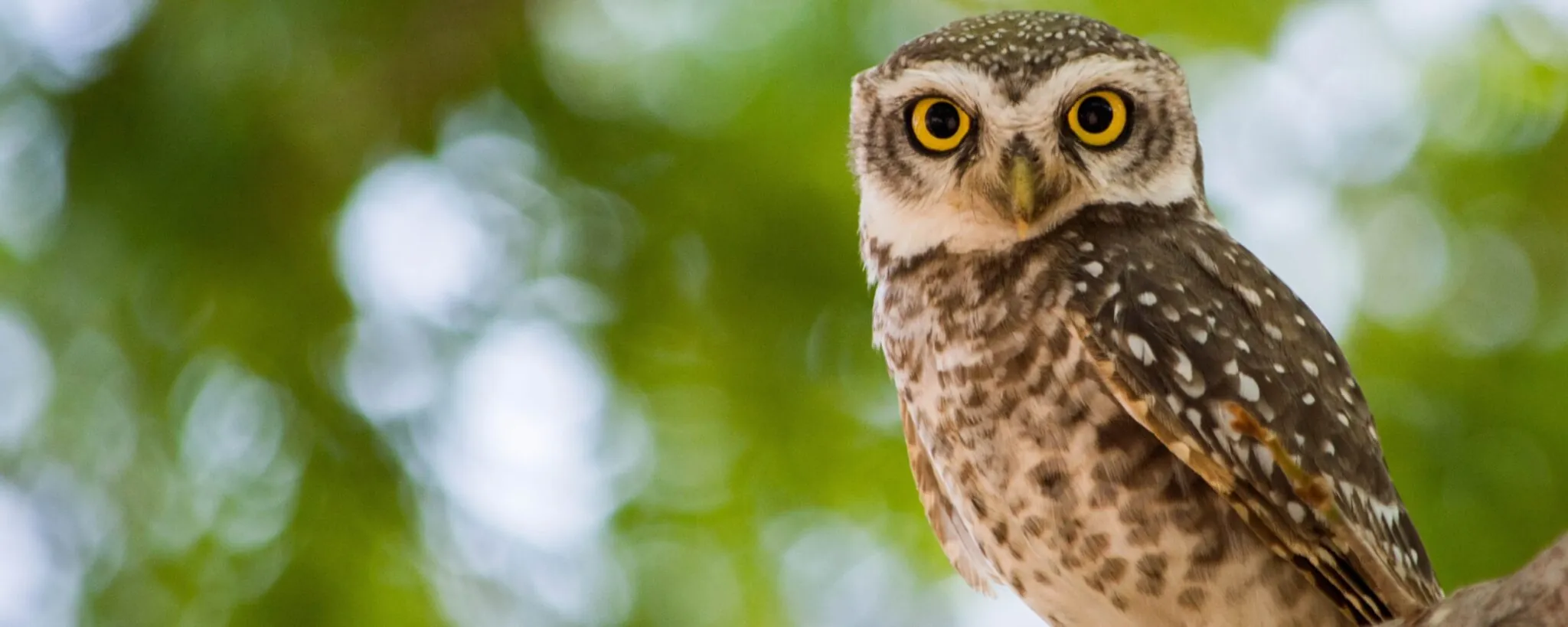
More than 40,000 species are threatened with extinction
At least 28% percent of all species on Earth face the possibility of extinction. That’s according to assessments by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). IUCN’s Red List of Threatened Species breaks down the risk by taxa.
These percentages are only of assessed species, of which there are more than 142,000. That’s a drop in the ocean when you realize there are an estimated 8.7 million species on Earth. We don’t actually know how many species are at risk.
Humans pose the biggest threat to biodiversity, but we are also the only species that can help address wide scale mass extinction. It’s not enough to talk about this crisis. We must focus on solutions. Through innovative conservation strategies, we can reverse the risk and save species.
Humans are the cause and solution
The current mass extinction event isn’t the first in Earth’s history. We’re living in the 6th mass extinction. But unlike previous events, humans are responsible for this one. Yet hope remains. “If working apart we’re a force powerful enough to destabilize our planet, surely, working together, we are powerful enough to save it,” said Sir David Attenborough.
IUCN Red List Assessors – including some staff members at the Global Center for Species Survival – look at a variety of direct threats when determining extinction risk. Threats include: