-
Menu
- Plan Your Visit
- Meet The Animals
- Check Out Events
- Memberships
- New in 2025 - Giant Tortoise
- About The Zoo
- Support the Zoo
- Conservation
- Education
- Groups & Private Events
- Zoo News
- Contact
- Zoo Store
- Indianapolis Prize
- Global Center for Species Survival
- Schedule
- Donate
- Membership
- Tickets

- Plan Your Visit
- Meet The Animals
- Check Out Events
- Memberships
- New in 2025 - Giant Tortoise
- About The Zoo
- Support the Zoo
- Conservation
- Education
- Groups & Private Events
- Zoo News
- Contact
- Zoo Store
- Indianapolis Prize
- Global Center for Species Survival

Cobras and Mambas
About
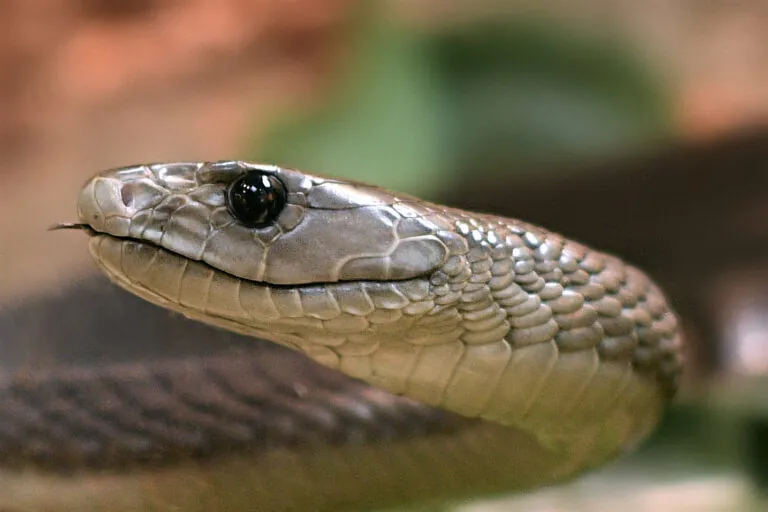
Cobras and mambas are members of a family of snakes called elapids that live in eastern and southern Africa. Elapids are venomous snakes with short fangs in the front of the mouth that don’t move. They use their fangs to bite their prey—a small animal—and their venom causes the prey to die so it can be eaten. Elapids usually live alone in trees or on the ground. Females lay eggs to reproduce. Cobras scare off predators by raising up and flaring their hood, skin that expands near their neck, and hissing. Mambas are the longest venomous snake in Africa!

Conservation
Many snakes are threatened with extinction because they were overhunted by people or from habitat loss. Snakes play important roles in ecosystems by keeping rodent populations under control. Be aware of snakes in your local area and give them their space in the wild. Always do your research before adopting a snake as a pet to be sure you can meet its needs for the entirety of its life.
WHERE ARE THEY AT THE ZOO?
Meet the Cobras and Mambas
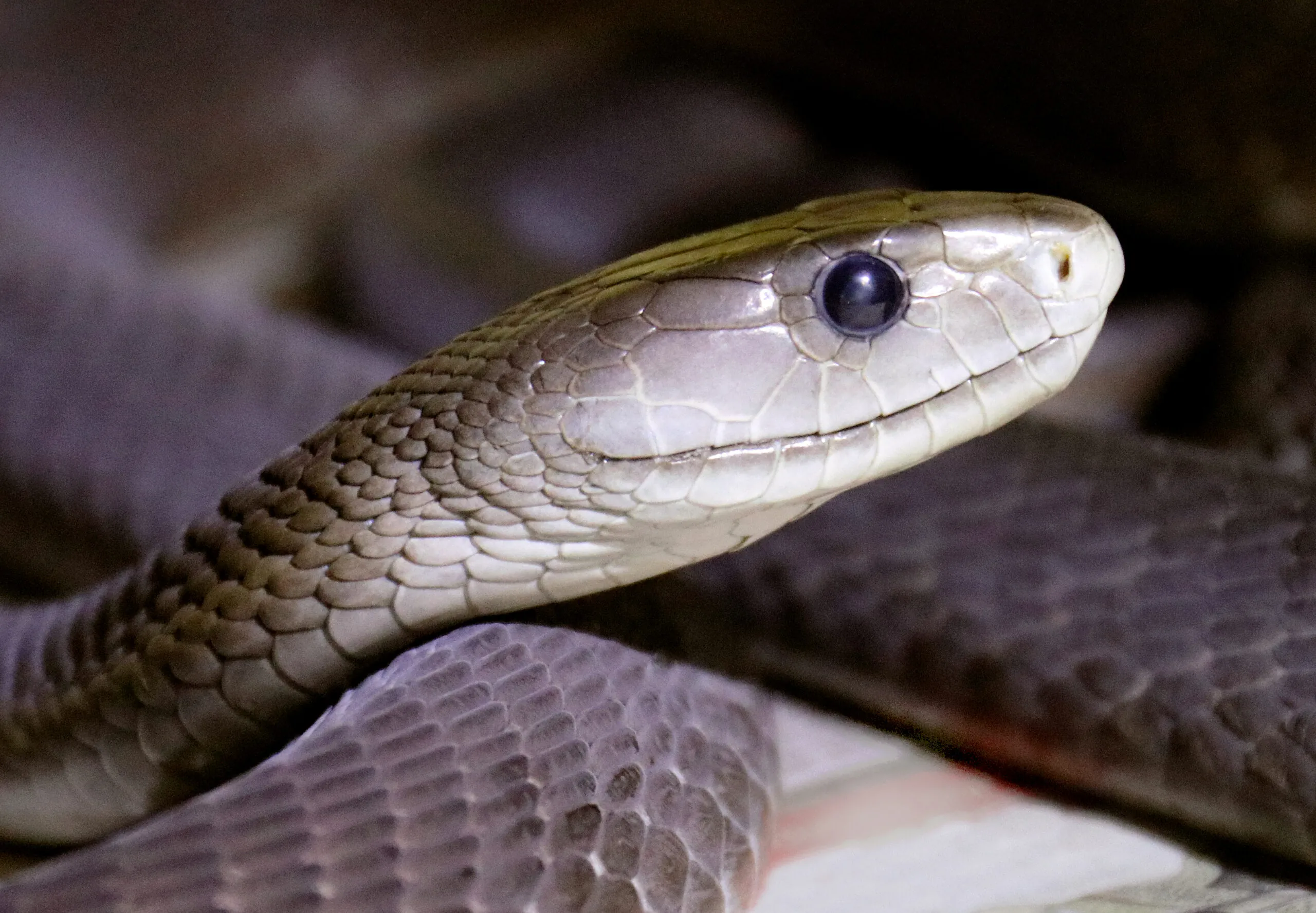

Lives in African woodlands/grasslands. Length: 8–14 ft. Grey with black mouth. IUCN Red List status: Least Concern
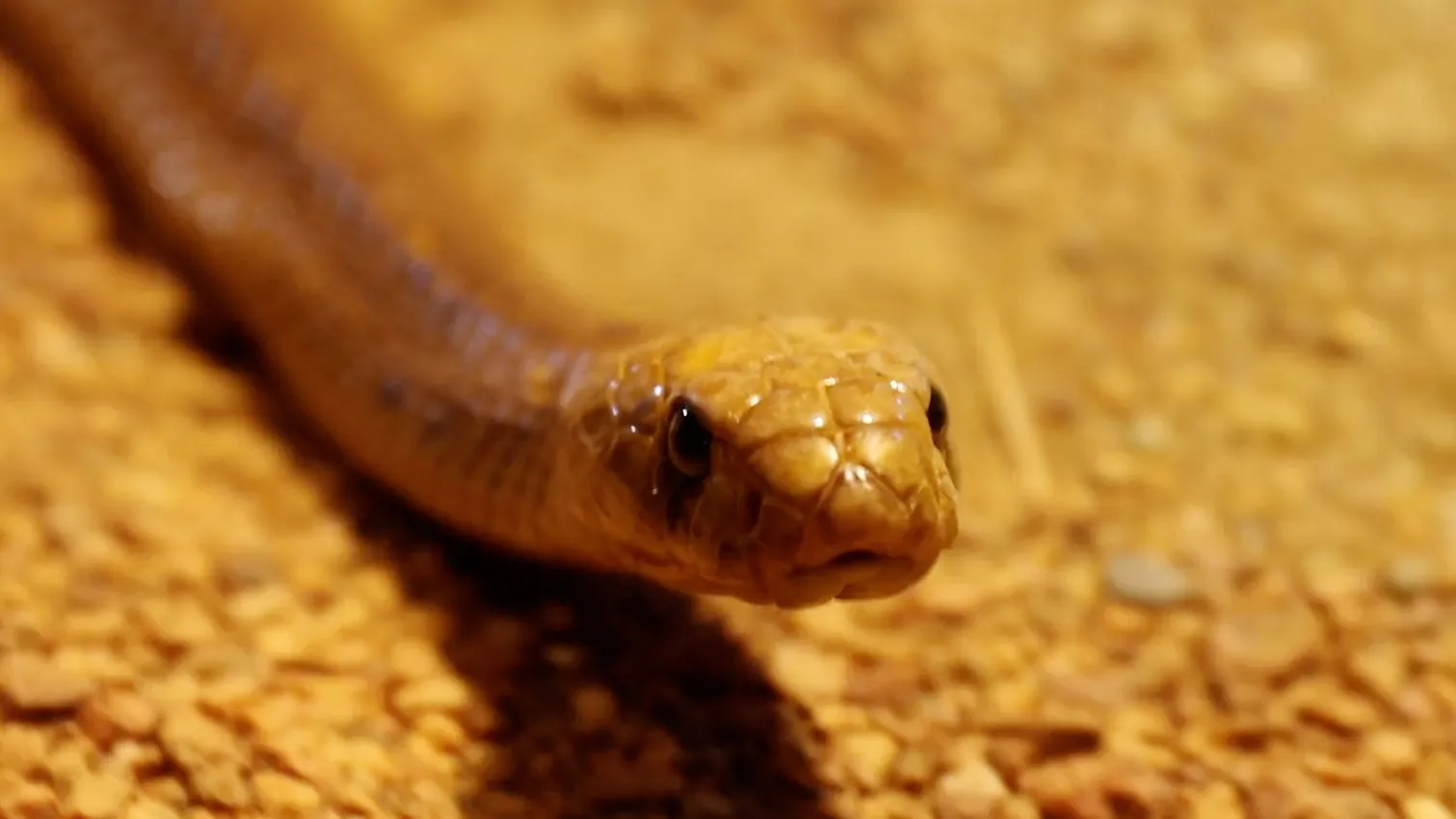

Lives in African grasslands. Length: 5 ft. Yellow, orange, brown or black. IUCN Red List status: Least Concern
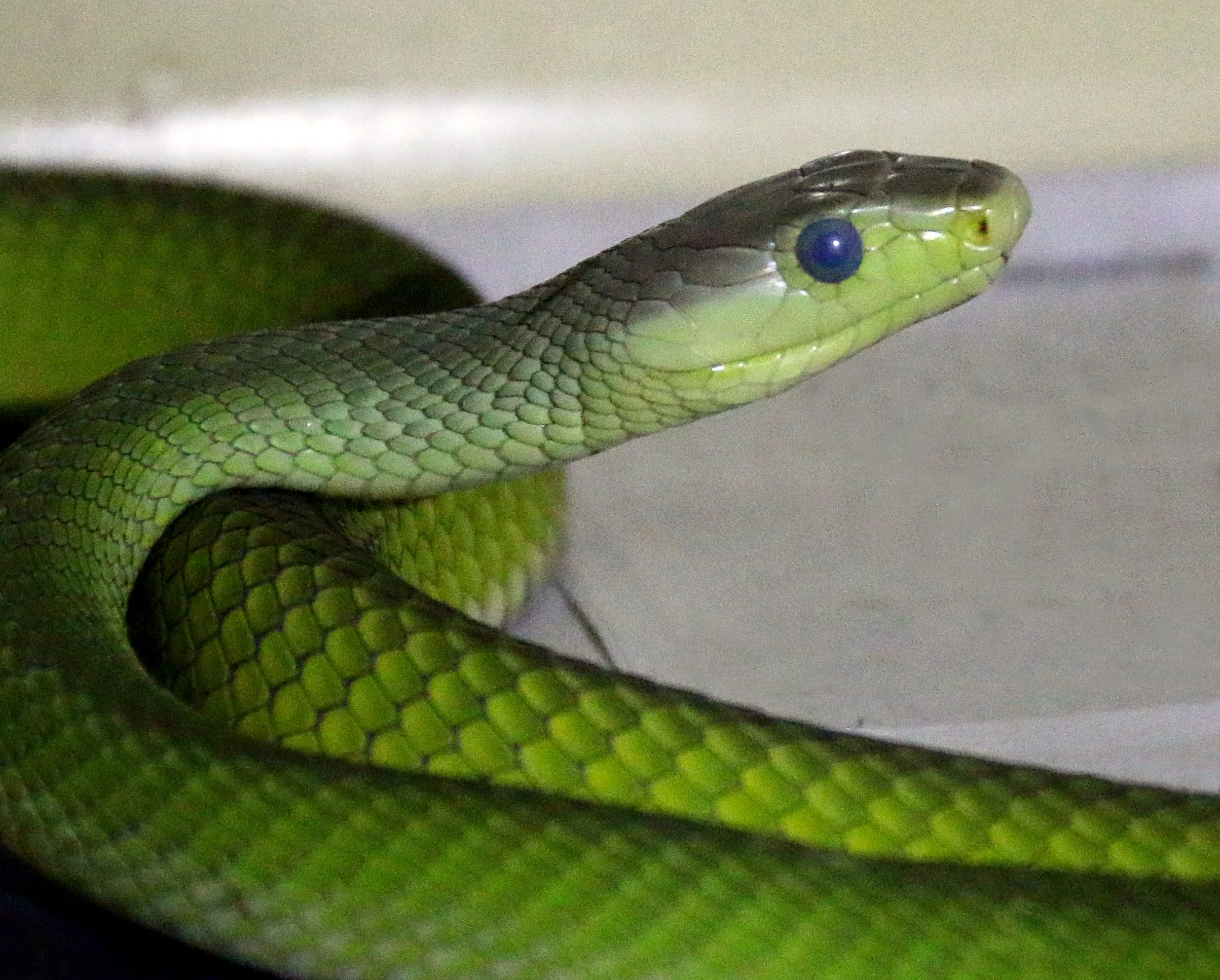

Lives in African forests/savannas. Length: 7 ft. Bright green. IUCN Red List status: Least Concern
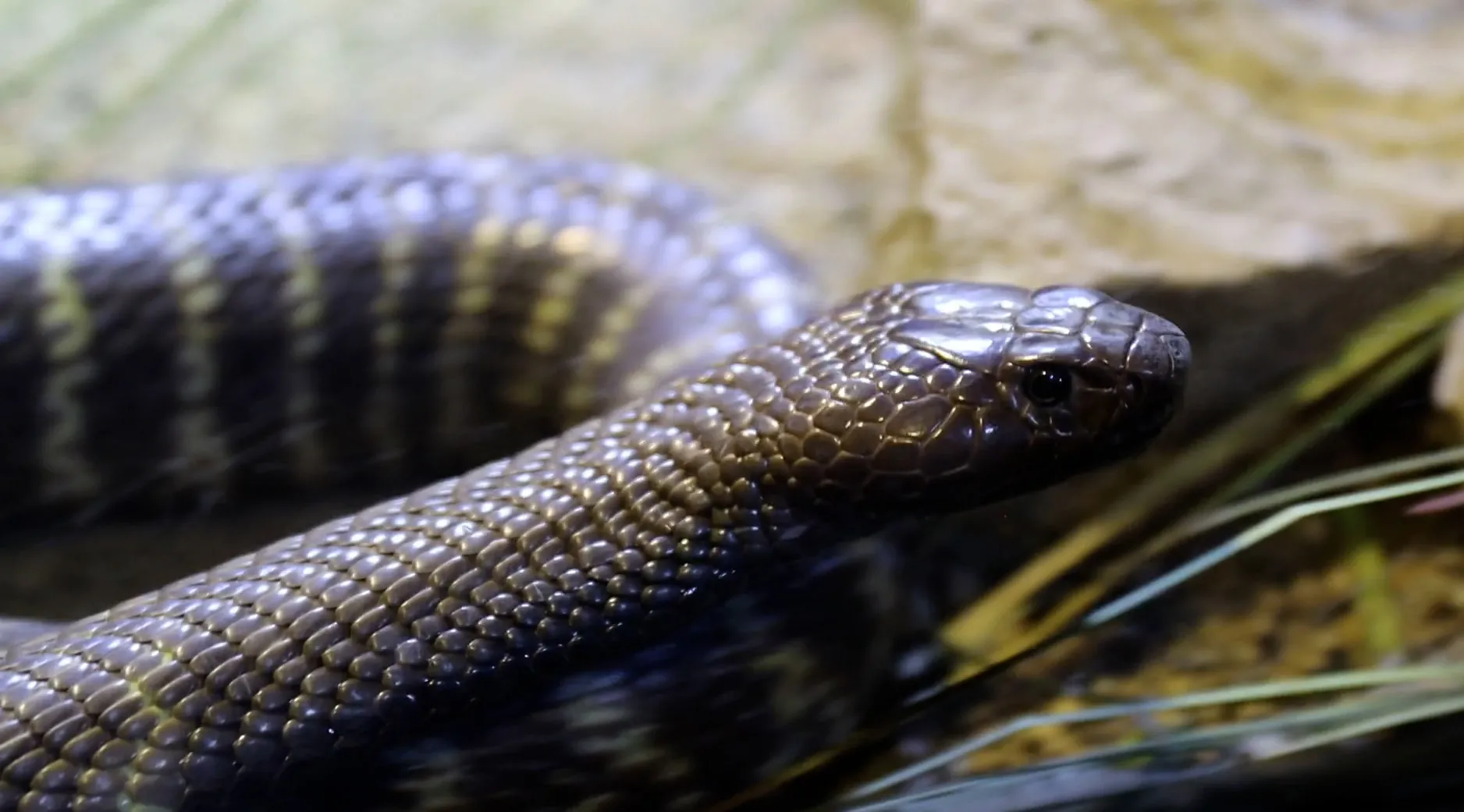

Lives in African grasslands. Length: 3 ft. Black and white, green or red bands. IUCN Red List status: Least Concern
